What is a Clinical Physiologist (Cardiac)?
A Clinical Physiologist (Cardiac) looks at how a patient’s heart works and can find out if there are any problems. They will be able to test if a patient’s heart does not beat correctly, or if there is a problem with the amount of blood flow to their heart, or if there is a problem other parts of their heart.
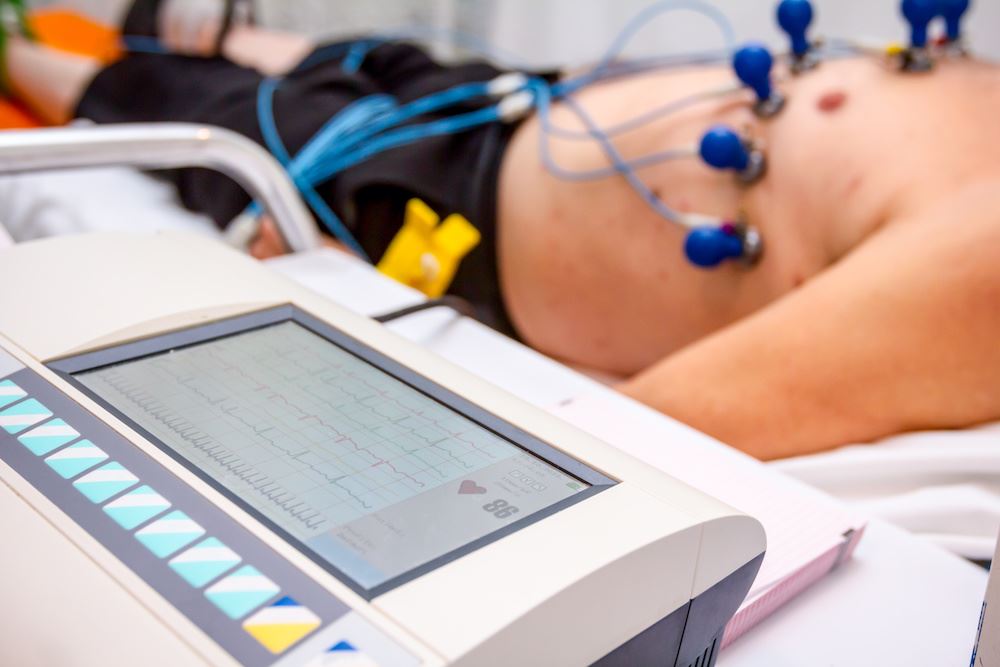 The Clinical Physiologist (Cardiac) may use any of the following tests when looking at how the heart works:
The Clinical Physiologist (Cardiac) may use any of the following tests when looking at how the heart works:
- Electrocardiography (ECG): An ECG is the most common test of how the heart works. The ECG looks at each heart beat to determine if there is a problem.
- An ECG recorded for a short time (for example, 5 minutes) is called a resting ECG. For a resting ECG the patient lies on a bed while sensors are attached to their arms, legs and chest to record the heart beats while the patient lies still.
- An ECG can also be recorded over a longer time (for example, 24 hours); this is called Ambulatory ECG or Holter monitoring. For an ambulatory ECG the patient wears the sensors for at least 24 hours, does their normal activities (at home and/or work), and the heart beats are recorded during this time.
- An ECG can also be recorded while a patient is exercising to see if the heart beats any differently during exercise. This type of testing is called an Exercise Stress Test.
- Cardiac Catheterisation Procedure: Cardiac catheterisation is an invasive test to see how well the heart is working. It is commonly used to look for blocked heart arteries (the hearts’ own blood supply) and is also used to measure the pressure inside different parts of the heart. During cardiac catheterisation heart blockages can be opened.
Specialist Clinical Physiologist (Cardiac) Testing
Clinical Physiologists (Cardiac) will need to do more training and study in order to do the following tests and procedures:
- Echocardiogram (Echo): Inside the heart there are many different parts that work to help pump blood around the body (for example, heart valves, heart muscles, heart chambers). An Echo is a test that uses ultrasound to take images (like photos) of the patient’s heart to see if the different parts of the heart are working properly.
- Cardiac Electrophysiology: Electrophysiology (EP) can measure the electrical function of the heart and also intervene to correct electrical activity in the heart.
- Implanted Cardiac Devices: When a patient’s heart is found to have abnormal activity that can lead to the heart pumping too fast or too slow a device such as a pacemaker or defibrillator can be implanted. A heart Doctor will implant the device and a cardiac physiologist is involved in testing the device and supporting the patient and their device in the long-term.
Find Out More.
If you would like to find out more information about heart health please see the following Australian website:
The Heart Foundation

 The Clinical Physiologist (Cardiac) may use any of the following tests when looking at how the heart works:
The Clinical Physiologist (Cardiac) may use any of the following tests when looking at how the heart works: 
